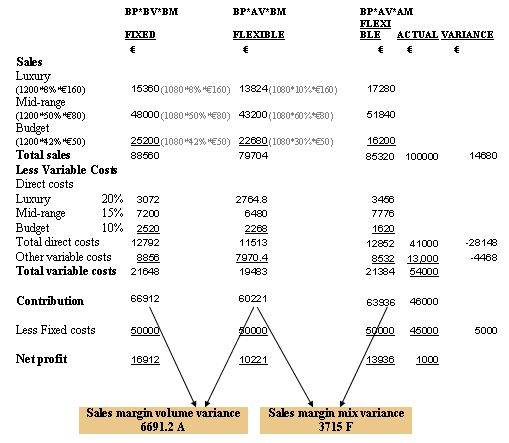
a) Prepare a statement showing the fixed budget, flexible budgets, actual results and variances for the quarter
This question has sales mix complications and thus a sales mix variance will have to be separately calculated. This is done by preparing a second flexible budget and comparing at contribution level the difference between the first flexible and second flexible budgets. The following approach is recommended
Step 1: Prepare the fixed budget. All the figures in the fixed budget are based on the original budget assumptions about sales price, sales volume and sales mix.
Budgeted price x budgeted volume x budgeted mix (BP x BV x BM)
Step 2: Prepare the flexible budget (flexible budget 1). This budget is based on actual volume sales, but at the original budgeted mix and budgeted prices. Any difference in contribution between the fixed and the flexible budget is due to the volume variance and hence this variance is isolated.
Budgeted price x actual volume x budgeted mix (BP x AV x BM)
Step 3: Prepare a second flexible budget (flexible budget 2). This budget is based on actual volume and the actual sales mix but at budgeted price. The difference in contribution between the first and second flexible budgets is due to the sales mix variance and hence this variance is isolated.
Budgeted price x actual volume x actual mix (BP x AV x AM)
Step 4: Enter the actual figures.
Actual price x actual volume x actual mix (AP x AV x AM)
Step 5: Find the price or cost variance. This is the difference between flexible budget 2 and actual figures.
b) Prepare a statement reconciling the budgeted net profit to the actual net profit
Statement reconciling budgeted net profit with actual net profit
BUDGETED NET PROFIT |
|
|
|
|
16912 |
|||||
Sales variances |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Sales margin volume variance |
|
-6691.2 |
|
|
|||||
|
Sales margin mix variance |
|
|
3715.2 |
|
|
||||
|
Sales price variance |
|
|
14680.0 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Direct cost |
|
|
|
-28148.0 |
|
|
||||
Other variable cost variance |
|
|
-4468.0 |
|
|
|||||
Fixed cost variance |
|
|
|
5000.0 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-15912 |
|||
ACTUAL NET PROFIT |
|
|
|
|
1000 |
|||||
c) Write a short report to the directors of the Doyle’s Hotel and Leisure Centre evaluating the results you have produced and suggesting possible reasons for the variances
In evaluating the performance of the business from the point of view of achieving budget targets this business has failed miserably. Actual profit has fallen 96% compared to the budget target. This suggests that either the budget targets were unachievable or random events outside the control of the business had a part to play in the actual performance. The following is an analysis of the variance calculated above.
Sales margin volume variance: Actual activity compared to budget fell 10% this caused a fall in profit of €6,691 or 39% (6691/16912). Management should investigate the reasons why sales volume was less than the budget target. Possible reasons include increased competition, increased prices, a contracting local and international economy and a budget target that was too easily achievable.
Sales margin mix variance: This is a positive variance of €3715 and is due to a big increase in demand for the mid-range category of accommodation whereas sales in the high cost luxury range fell. This variance ensured profit increased by 22% and management must assess the reasons why the sales mix changed so significantly.
Sales price variance. The is no break down of the average room rate for each category of accommodation. Overall however this is a positive variance of €14,680 amount to 87% of budgeted profit. This is a very significant variance and management should identify why and what accommodation types managed to achieve higher room rates that the target. This variance can be related to the negative volume variance. When a price increases volume sales can decrease. Overall the positive price variance is greater than the negative volume variance. Management should evaluate their budgeted room rates to see if they were too easily achievable.
The direct cost variance is the largest variance and is negative. The variance amounts to €28,148 and is 1.66 times the budgeted profit figure. Management need to investigate this variance as it is at the centre of the poor operational performance. What costs are included here and why was there so high a variance. This variance on its won would have ensured the business achieved an actual net loss of €11230. Was this variance due to poor forecasting, operational inefficiencies and poor management in controlling direct costs or random occurrences management need to investigate and take quick corrective action?
Other variable costs increased by 26% compared to budget. This lead to a negative variance of €4468 or 30% of budgeted profit. Management need to break-down this category of expense and assess what expense items increased and why. Again the budget target must be examined and process of agreeing budget target questioned.
Fixed costs fell by 10% compared to budget amounting to a positive variance of €5,000. Management need to break-down fixed costs into each category of expense and assess what expense items increased and why. Again the budget target must be examined and process of agreeing budget target questioned.