a) Prepare a budgetary control statement showing fixed and flexible budgets with actual results and variances
The following steps can be taken:
- Layout the budgetary control statement, clearly labeling each column and use a marginal costing format.
- Enter the fixed budget figures
- Calculate and enter the flexible budget figures. Remember both sales and variable costs should be the actual volume multiplied by the budgeted unit information but the fixed costs are left unchanged. In this question there are two items involved multiply each volume by the relative price / cost.
- Enter the actual figures. Remember to separate semi-variable costs.
- Calculate the variances
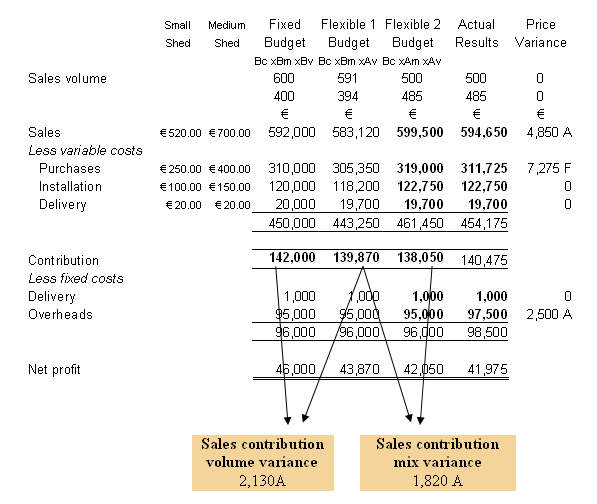
Statement reconciling budgeted net profit with actual
|
€ |
€ |
Budgeted Net profit Sales price variance Sales contribution volume variance Sales contributions mix variance Purchases variance Overheads variance |
4,850 A 2,130 A 1,820 A 7,275 F 2,500 A |
46,000
_4,025 |
Actual Net profit |
|
41,975 |
b) Discuss the position revealed by the statement.
Overall the actual net profit was €4025 or 8.75% less than budgeted. The main variances identified above show that the sales variances are the main cause for this adverse overall variance. There is also a significant increase in overheads compared to the budget target
Sales price variance : This is a negative variance of €4,850 due to the fact that the company did not achieve its sales price targets.. Possible reasons include increased competition a well as the possibility that the budget price targets were overly optimistic.
Sales contribution volume variance : This is also a negative variance as the company sold less units than budgeted. Actual sales were 1.5% less than target. Again management need to assess reasons for this variance including questioning the target figure of 1000 units for the period.
Sales contribution mix variance : This is also a negative variance due to the actual sales mix differing from the budgeted sales mix. The company most profitable shed is the small shed as it costs less and has less installation time. The company budgeted to sell 600 units of the small shed however actual sales were 500 units a drop of 16.7%. This is the reason for this negative variance.
Purchases cost variance : Purchase costs fell in this period. Actual purchase costs were €7275 or 2.28% less than the budget target. This is the only positive variance for the period. Management must understand the reasons behind this variance. Was it due to the target purchase costs not being realistic or the fact that the company achieve unexpected savings in this area.
Overhead variance : This is a negative variance of €2,500 where actual overhead was €2,500 or 2.63% above the budget target. Management should analyse the break-down of overheads to identify what actual overhead item varied above the target and assess the reasons behind this.